Unveiling the Cause: A Journey Through Female Hair Thinning
Table Of Content
- What is hair thinning and what various factors contribute to hair thinning?
- Treatment & suggestion of hair thinning.
- Hair transplantation for thinning hair.
What is hair thinning and what various factors contribute to hair thinning?
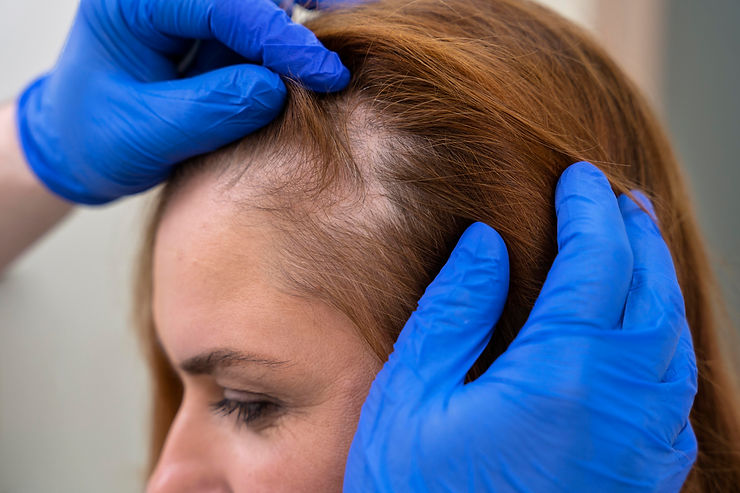
Hair thinning in females can be a distressing experience, affecting self-esteem and quality of life. Understanding the underlying causes of female hair thinning is crucial for effective management and treatment. This article takes you on a journey to explore the various factors that contribute to hair thinning in women, shedding light on possible root causes.
Hormonal Imbalances
1. Menopause: Fluctuations in hormone levels during menopause can lead to hair thinning. Reduced estrogen and progesterone levels and increased androgen activity can negatively impact hair growth.
2. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS, a hormonal disorder, can cause excessive androgen production, leading to hair thinning in women. Insulin resistance associated with PCOS further exacerbates the condition.
Genetic Predisposition:
1. Female Pattern Hair Loss (FPHL): Similar to male pattern baldness, FPHL is a hereditary condition. It causes progressive hair thinning, primarily at the crown and frontal areas, due to a genetic sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Nutritional Deficiencies:
1. Iron deficiency: Insufficient iron levels can hinder proper hair growth, leading to hair thinning. Iron is essential for carrying oxygen to the hair follicles.
2. B-vitamin deficiency: Lack of essential B vitamins, such as biotin, niacin, and vitamin B12, can impact hair health and contribute to thinning.
Stress and Emotional Factors:
1. Telogen Effluvium: Severe stress, emotional trauma, or physical illness can trigger telogen effluvium, a condition where hair prematurely enters the resting (telogen) phase, causing excessive shedding and subsequent hair thinning.
Hairstyling Practices:
1. Traction Alopecia: Constantly pulling the hair tightly through hairstyles like braids, ponytails, or extensions can lead to traction alopecia. Over time, this can cause hair thinning and even permanent hair loss in affected areas.
Medical Conditions and Medications:
1. Thyroid disorders: Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to thinning.
2. Medications: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, anticoagulants, and some antidepressants, may have hair thinning as a side effect.
Treatment & suggestion of hair thinning.
Consultation with a Dermatologist or Hair Specialist: If you’re experiencing hair thinning, it’s advisable to seek professional help. A dermatologist or hair specialist can assess your condition, determine the underlying cause, and provide appropriate treatment recommendations.
1. Medications and Topical Treatments: FDA-approved medications like minoxidil (Rogaine) can be used to promote hair regrowth and slow down further thinning. It’s available as a topical solution or foam and is typically applied directly to the scalp. Prescription medications, such as finasteride (Propecia), may be recommended for women with androgenetic alopecia. These medications work by blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT, a hormone that contributes to hair thinning. Topical corticosteroids or anti-inflammatory creams can be prescribed to manage conditions like scalp inflammation or autoimmune-related hair loss.
2. Nutritional Supplements: Nutritional deficiencies can contribute to hair thinning, so it’s important to maintain a balanced diet. Consider including foods rich in vitamins A, C, E, biotin, zinc, and iron. However, consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplements.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves extracting the patient’s blood, processing it to isolate platelet-rich plasma, and injecting it into the scalp. PRP contains growth factors that can stimulate hair growth and improve hair thickness.
4. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): LLLT utilizes red light to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair regrowth. This treatment can be performed using handheld devices or in-clinic laser caps or helmets.
5. Hair Care Practices: Be gentle with your hair to avoid further damage or breakage. Use a wide-toothed comb or a brush with soft bristles to minimize pulling and tugging. Avoid excessive heat styling and harsh chemical treatments that can weaken and damage the hair.
Choose hair care products formulated for thinning hair, including volumizing shampoos and conditioners.
6. Stress Management: Excessive stress can contribute to hair thinning. Explore stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, exercise, and yoga, or seek professional help if needed.
7. Hairstyling Considerations: Avoid hairstyles that exert excessive tension on the hair, such as tight ponytails, braids, or extensions. Opt for looser styles that minimize traction and stress on the hair follicles.
Hair transplantation for thinning hair
Hair transplants can be an option for individuals with hair thinning, particularly those with localized areas of thinning or baldness. Hair transplant procedures involve taking hair follicles from a donor area (typically the back or sides of the scalp) and implanting them into the thinning or balding areas.
Hair transplants can provide natural-looking results and effectively restore hair density in areas affected by thinning. However, it’s important to note that not everyone with hair thinning may be a suitable candidate for a hair transplant. Factors such as the extent of hair loss, the availability of the donor’s hair, and the stability of hair loss should be considered during the evaluation process.
It is recommended to consult with a qualified hair transplant specialist who can assess your specific situation, determine if you are a suitable candidate for a hair transplant, and discuss the potential benefits and limitations of the procedure. They can guide you in making an informed decision based on your individual needs and expectations.